Introduction to Vegan Superfoods
Superfoods have become a buzzword in the health and wellness community, and for good reason. These nutrient-dense foods are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can significantly enhance your overall well-being. For individuals following a vegan diet, incorporating a variety of superfoods is essential to ensure they receive all the necessary nutrients for optimal health. Vegan superfoods, in particular, are plant-based powerhouses that provide a wide array of benefits, from boosting energy levels to improving immune function.
Nutrient density is a key characteristic of superfoods, meaning they offer a high amount of nutrients relative to their calorie content. This makes them an excellent choice for those looking to maximize the nutritional value of their meals without consuming excess calories. Antioxidants, another crucial component of superfoods, help combat oxidative stress and inflammation, reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
The following list comprises common and widely available vegan superfoods that can easily be incorporated into daily meals. From leafy greens rich in iron and calcium to seeds and nuts bursting with omega-3 fatty acids, these superfoods offer a diverse range of flavors and textures to keep your diet exciting and satisfying. Whether you are a seasoned vegan or just starting out, these superfoods can help elevate your nutrition game to the next level.
As we delve into the top 30 vegan superfoods, you’ll discover foods that not only taste great but also provide a multitude of health benefits. By including these superfoods in your diet, you can significantly improve your overall health, energy levels, and well-being. Let’s embark on this journey to uncover the nutritional treasures that vegan superfoods have to offer.
Kale: The Leafy Green Overachiever
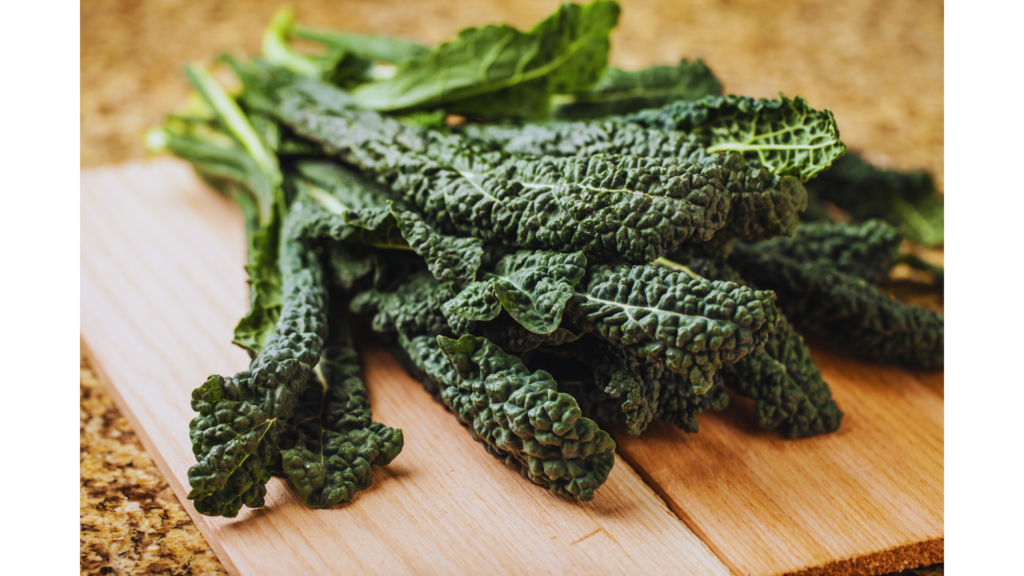

Kale is like the valedictorian of leafy greens—it’s always at the top of the class. But did you know that kale contains more vitamin C per calorie than an orange? That’s right, this green giant is a stealthy immune booster. It’s also packed with lutein and zeaxanthin, antioxidants that protect your eyes from blue light damage (perfect for those of us glued to our screens).
Pro Tip: Massage your kale with a bit of lemon juice and olive oil to break down its tough fibers. Your salads will thank you.
Blueberries: The Brain’s Best Friend
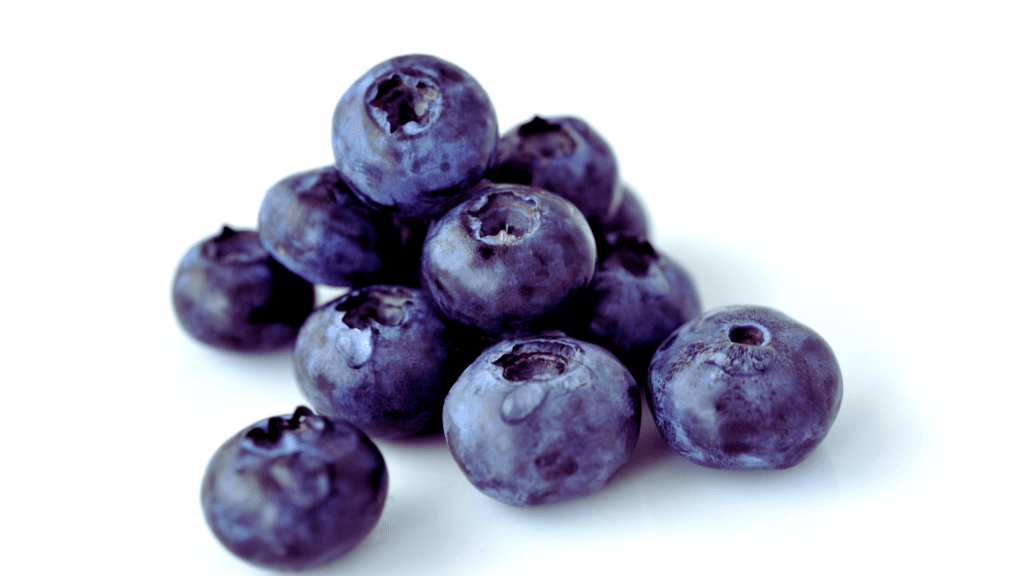

Blueberries are tiny but mighty, and their deep blue hue comes from anthocyanins, antioxidants that have been shown to improve memory and cognitive function. A 2019 study published in Nutrition Reviews found that regular blueberry consumption can slow brain aging by up to 2.5 years. Who needs a fountain of youth when you’ve got a bowl of blueberries?
Fun Fact: Blueberries are one of the few fruits native to North America. Native Americans called them “star berries” because of the star-shaped calyx on each berry.
Quinoa: The Protein-Packed Grain
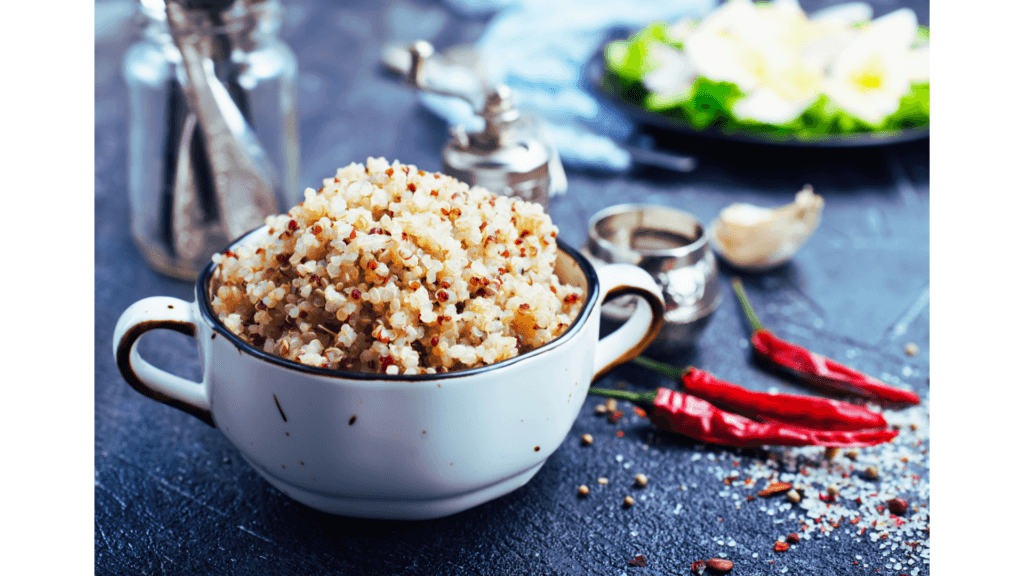

Quinoa isn’t just a grain—it’s a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids. This makes it a staple for vegans looking to build muscle or simply stay full longer. Plus, it’s gluten-free and rich in magnesium, a mineral that helps relax muscles and reduce stress.
Pro Tip: Rinse quinoa thoroughly before cooking to remove its natural coating of saponins, which can taste bitter.
Chia Seeds: The Tiny Energy Bombs
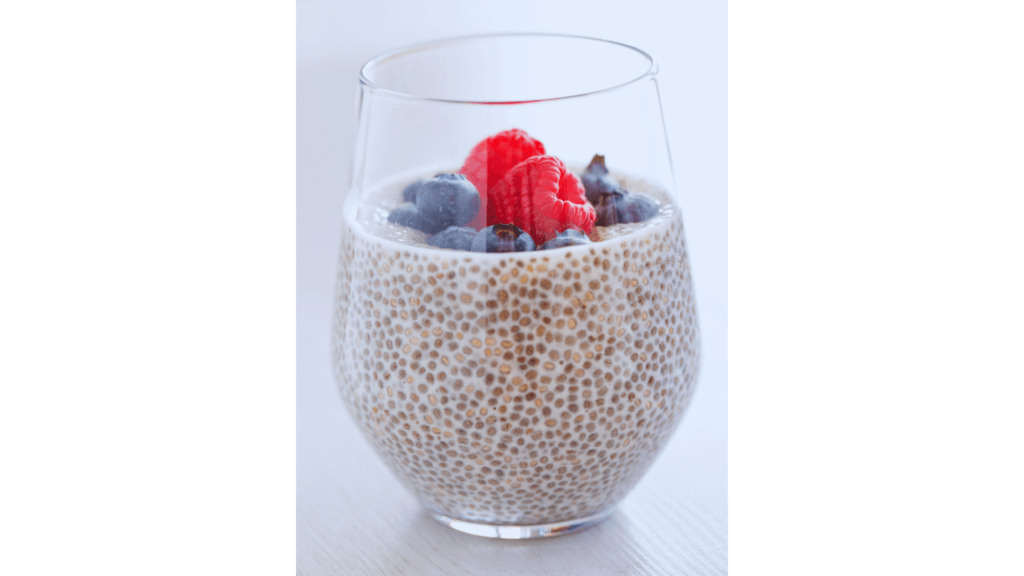

Chia seeds are like the Swiss Army knife of superfoods. They’re loaded with omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and protein, and they can absorb up to 10 times their weight in water, making them a great natural thickener for puddings and smoothies.
Fun Fact: Chia seeds were a staple of the Aztec diet and were even used as currency. Talk about a valuable snack!
Spinach: Popeye Was Onto Something
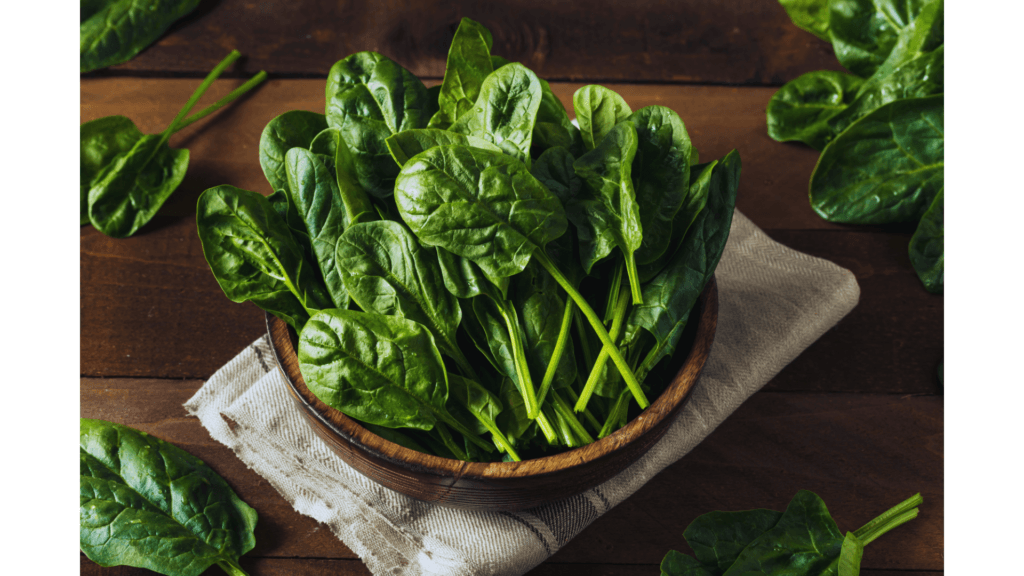

Spinach is a nutritional powerhouse, but here’s something you might not know: it’s one of the best plant-based sources of non-heme iron. Pair it with vitamin C-rich foods (like bell peppers or citrus) to boost iron absorption.
Pro Tip: Add a handful of spinach to your morning smoothie. You won’t even taste it, but your body will reap the benefits
Avocado: The Creamy Heart-Protector
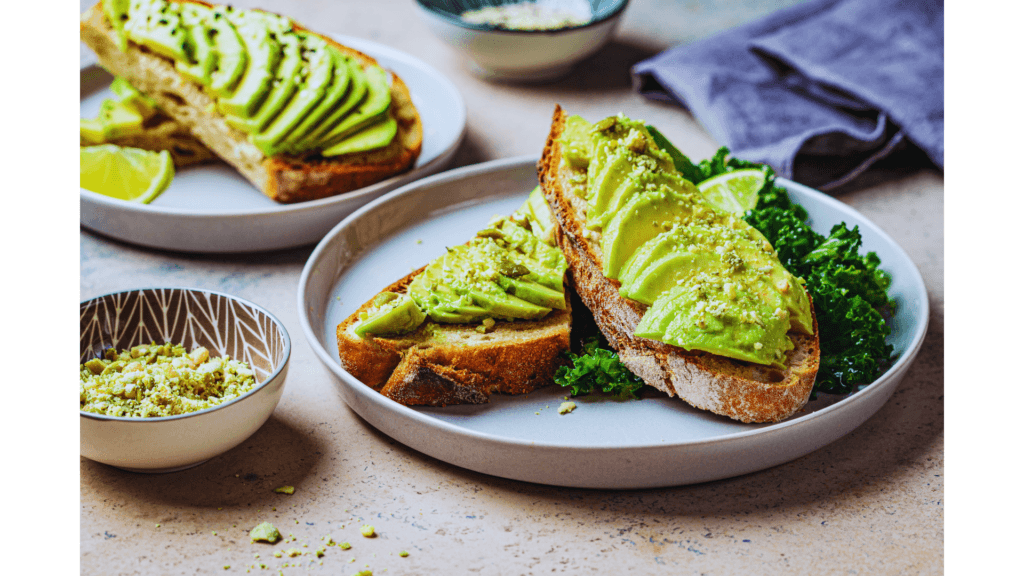

Avocados are rich in monounsaturated fats, which can help lower bad cholesterol levels. But did you know they also contain more potassium than bananas? Potassium is essential for heart health and muscle function.
Fun Fact: Avocados are technically berries. Yes, you’ve been eating berry toast all along.
Sweet Potatoes: The Beta-Carotene Bonanza
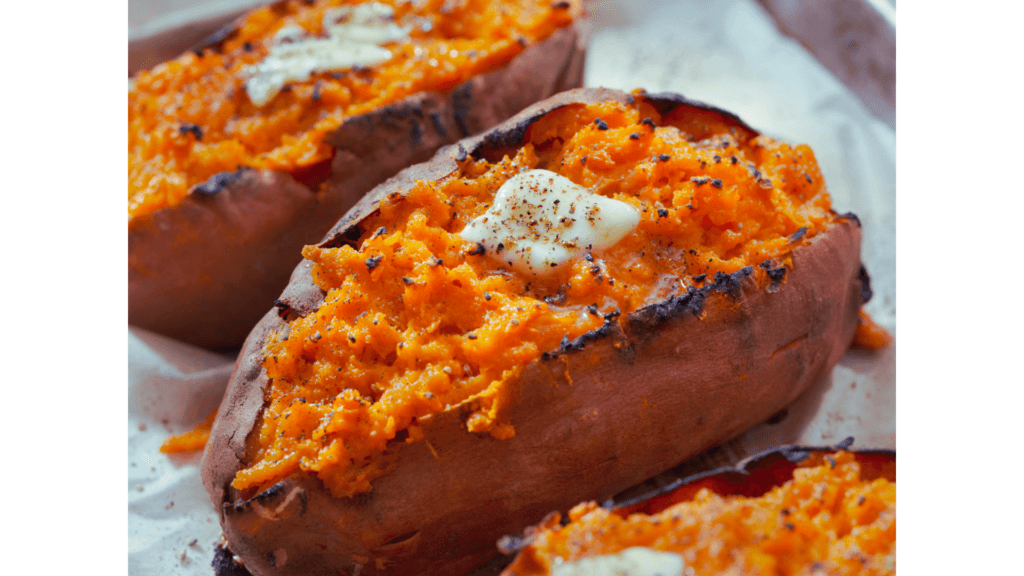

Sweet potatoes are loaded with beta-carotene, which your body converts into vitamin A. Just one medium sweet potato provides over 400% of your daily vitamin A needs. They’re also a great source of resistant starch, which feeds your gut bacteria and supports digestion.
Pro Tip: Bake sweet potatoes whole and top them with black beans, salsa, and a dollop of vegan sour cream for a quick, nutrient-packed meal
Almonds: The Snack That Loves You Back
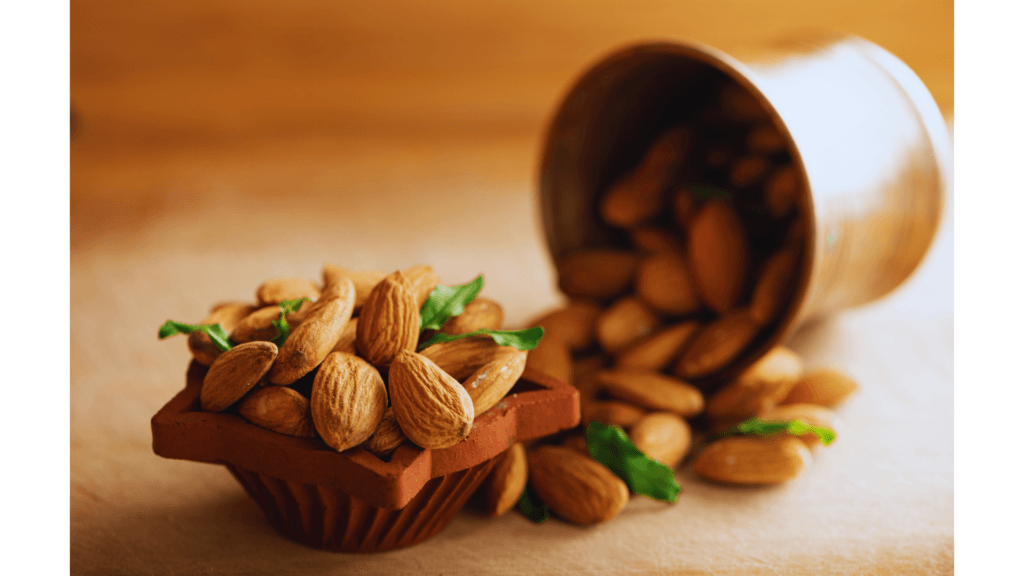

Almonds are a great source of vitamin E, a powerful antioxidant that protects your skin from UV damage. They’re also rich in magnesium, which can help reduce stress and improve sleep quality.
Fun Fact: It takes about 1.1 gallons of water to grow a single almond. While they’re nutritious, it’s worth considering their environmental impact and opting for sustainably sourced varieties.
Lentils: The Protein Powerhouse

Lentils are a vegan’s best friend, offering 18 grams of protein per cooked cup. They’re also rich in folate, a B-vitamin that’s crucial for brain health and energy production.
Pro Tip: Use lentils as a meat substitute in tacos, burgers, or spaghetti bolognese. Their hearty texture makes them a versatile addition to any dish.
Broccoli: The Detox Dynamo

Broccoli contains sulforaphane, a compound that activates your body’s natural detoxification enzymes. Studies have shown that sulforaphane can help reduce the risk of certain cancers and support liver health.
Fun Fact: Broccoli is a member of the cabbage family, which also includes kale, Brussels sprouts, and cauliflower. It’s basically the cool cousin at the family reunion.
Walnuts: The Brain-Boosting Nut

Walnuts are the only nuts with a significant amount of omega-3 fatty acids, specifically alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which is essential for brain health. Studies have shown that eating walnuts can improve cognitive function and even reduce symptoms of depression. Plus, their wrinkly shape looks like a tiny brain—coincidence? I think not.
Fun Fact: Ancient Romans believed walnuts were a gift from the gods and used them as a symbol of fertility.
Pro Tip: Add crushed walnuts to your oatmeal or vegan banana bread for a crunchy, brain-boosting twist.
Flaxseeds: The Fiber-Filled Wonder

Flaxseeds are a powerhouse of lignans, antioxidant compounds that have been linked to a reduced risk of breast cancer. They’re also one of the best plant-based sources of omega-3s and fiber, making them a must-have for heart health and digestion.
Fun Fact: Flaxseeds were used in ancient Egypt as a laxative. Thankfully, they’re much tastier in modern smoothies and baked goods.
Pro Tip: Grind flaxseeds before eating to unlock their full nutritional potential. Sprinkle them on salads, soups, or yogurt alternatives.
Ginger: The Spicy Healer
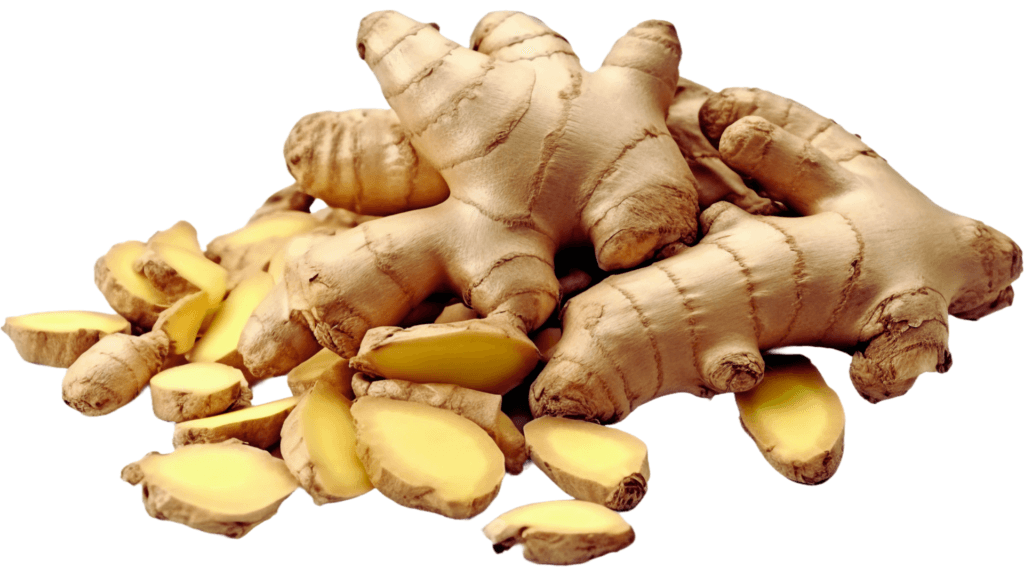

Ginger is more than just a sushi sidekick. It contains gingerol, a bioactive compound with potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Research shows ginger can ease nausea, reduce muscle pain, and even lower blood sugar levels.
Fun Fact: Ginger has been used for over 5,000 years in traditional medicine. It was so valuable in the Middle Ages that a pound of ginger cost the same as a whole sheep.
Pro Tip: Add fresh ginger to your morning smoothie or steep it in hot water for a soothing tea.
Turmeric: The Golden Anti-Inflammatory
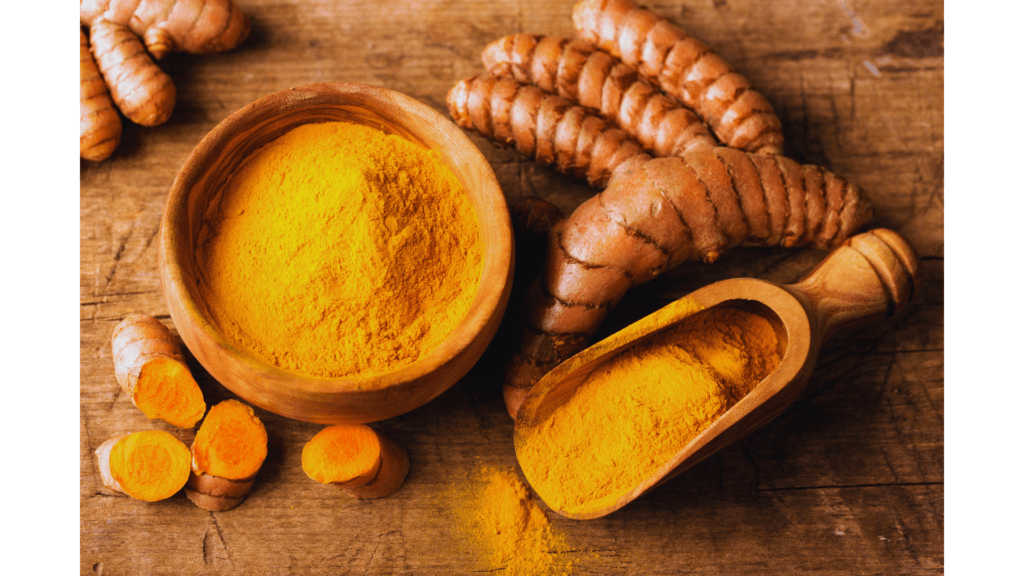

Turmeric’s vibrant yellow color comes from curcumin, a compound with powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Studies suggest curcumin can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and Alzheimer’s.
Fun Fact: Turmeric has been used in Ayurvedic medicine for over 4,000 years. It’s also a natural dye—so don’t spill it on your white shirt!
Pro Tip: Pair turmeric with black pepper to boost curcumin absorption by up to 2,000%
Garlic: The Immune System’s Best Friend
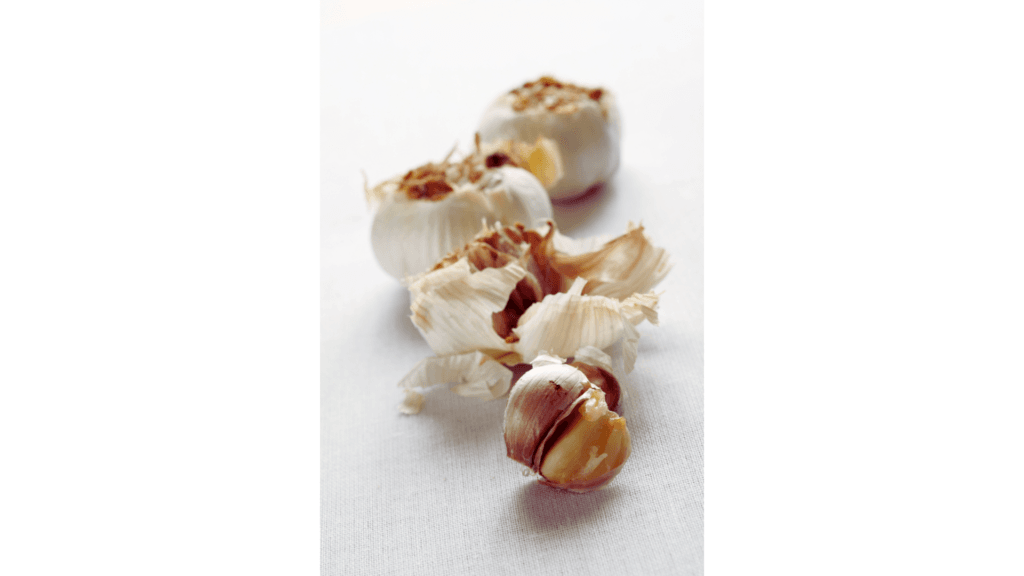

Garlic isn’t just for keeping vampires away. It contains allicin, a sulfur compound that has been shown to boost immune function and reduce the risk of heart disease. Plus, it’s a natural antibiotic.
Fun Fact: Ancient Egyptian workers building the pyramids were given garlic to keep them strong and healthy. Talk about an ancient superfood!
Pro Tip: Crush or chop garlic and let it sit for 10 minutes before cooking to activate its health-boosting compounds.
Beetroots: The Athletic Performance Enhancer
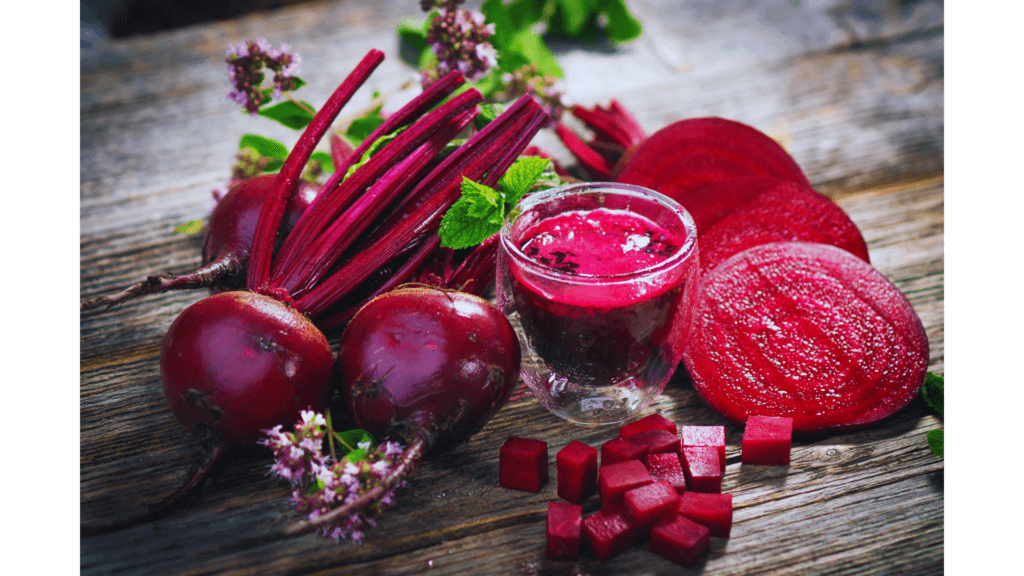
Beetroots are rich in nitrates, which your body converts into nitric oxide. This compound improves blood flow, lowers blood pressure, and enhances athletic performance. Studies show that drinking beetroot juice can increase endurance by up to 16%.
Fun Fact: Beetroots were used as a natural dye in the 19th century, and their juice was even used as a blush by Victorian women.
Pro Tip: Roast beetroots with a drizzle of balsamic vinegar for a sweet and savory side dish.
Hemp Seeds: The Complete Protein
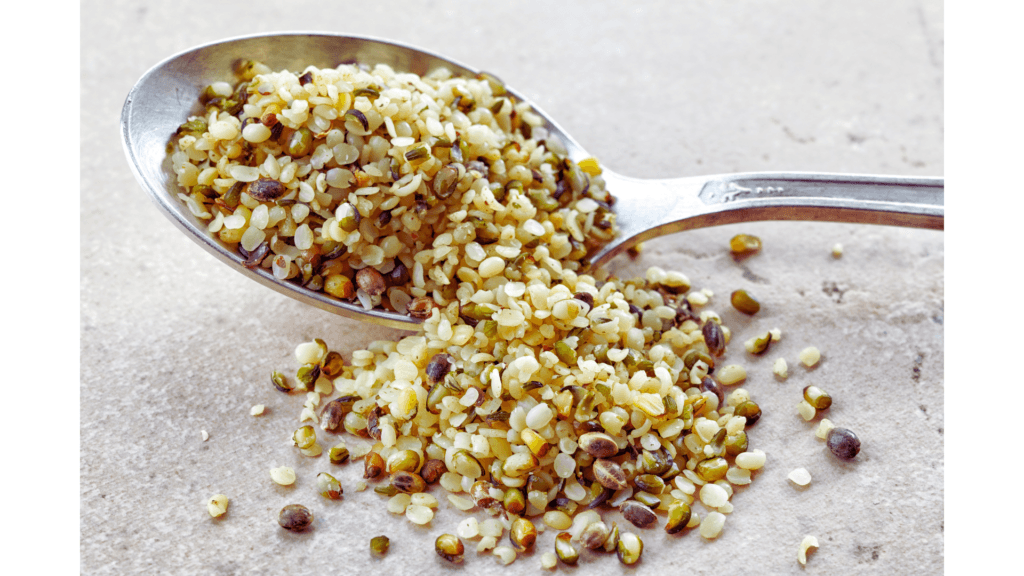

Hemp seeds are a complete protein, meaning they contain all nine essential amino acids. They’re also rich in omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, making them a great addition to a vegan diet.
Fun Fact: Hemp seeds are technically nuts, not seeds. They’re also one of the oldest cultivated crops, dating back over 10,000 years.
Pro Tip: Sprinkle hemp seeds on salads, soups, or avocado toast for a nutty crunch.
Pumpkin Seeds: The Sleep Supporter
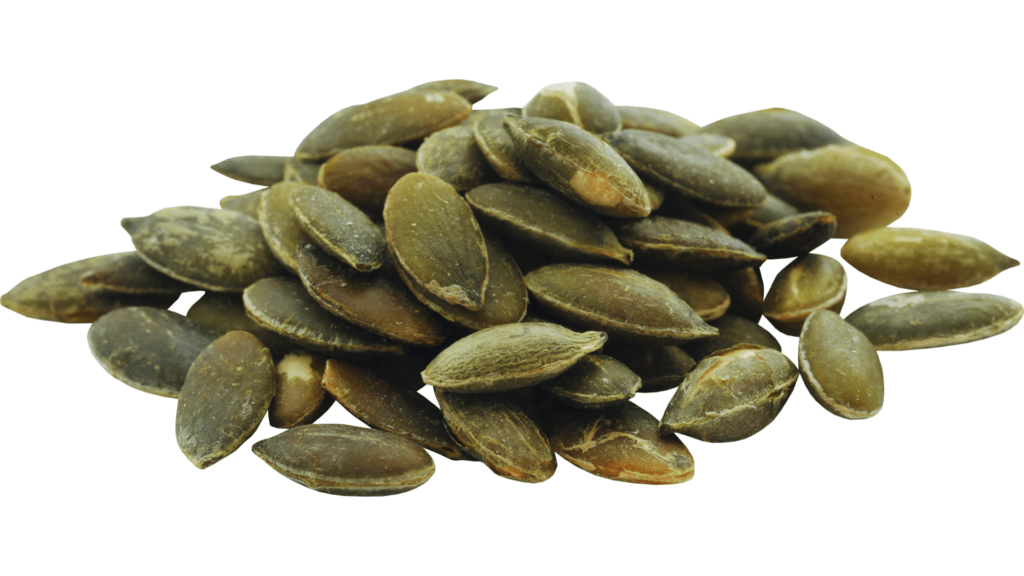

Pumpkin seeds are packed with magnesium, a mineral that helps regulate sleep and reduce stress. They’re also high in zinc, which supports immune function and skin health.
Fun Fact: Pumpkin seeds were a staple of Native American diets and were even used as a natural remedy for parasites.
Pro Tip: Toast pumpkin seeds with a sprinkle of smoked paprika for a savory snack.
Pomegranates: The Heart-Protective Fruit
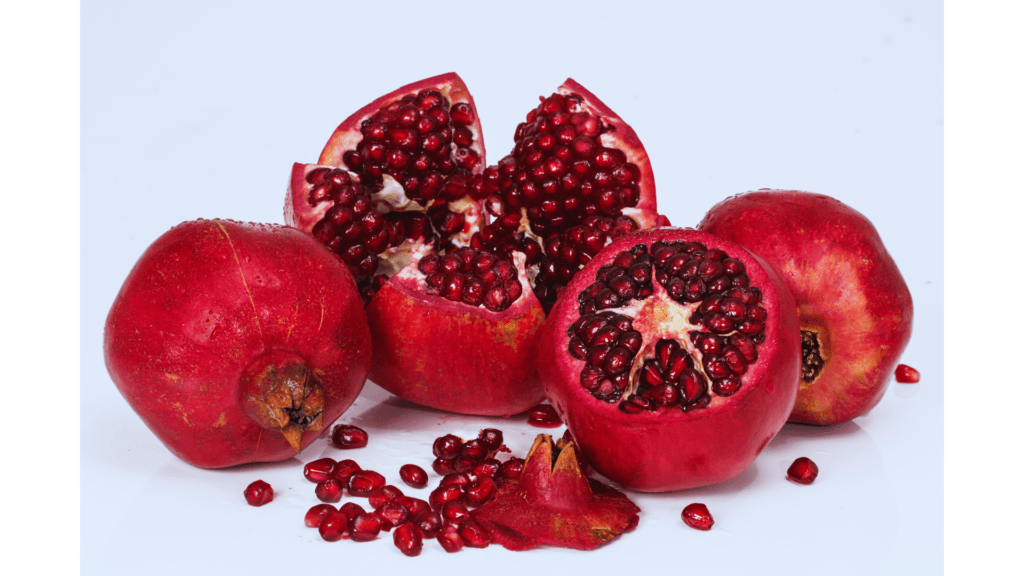

Pomegranates are rich in punicalagins, antioxidants that have been shown to reduce inflammation and protect against heart disease. Their juice has three times more antioxidants than green tea or red wine.
Fun Fact: In Greek mythology, pomegranates were considered a symbol of fertility and abundance.
Pro Tip: Add pomegranate seeds to your morning oatmeal or salads for a burst of color and flavor.
Brussels Sprouts: The Cruciferous Powerhouse
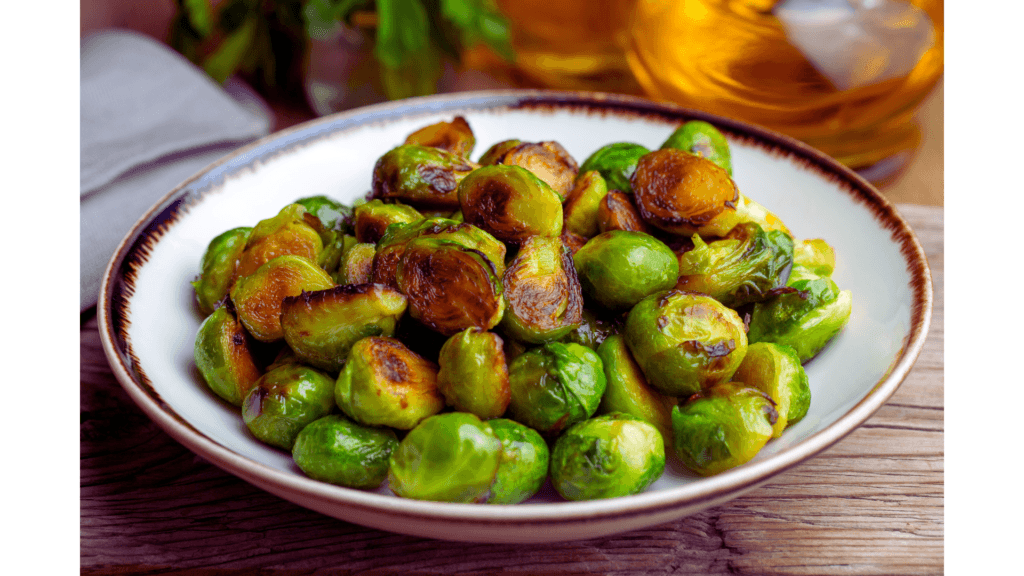

Brussels sprouts are high in glucosinolates, compounds that support detoxification and reduce inflammation. They’re also a great source of vitamin K, which is essential for bone health.
Fun Fact: Brussels sprouts were first cultivated in ancient Rome, but they got their name from being popular in Brussels, Belgium.
Pro Tip: Roast Brussels sprouts with a drizzle of maple syrup and a sprinkle of chili flakes for a sweet and spicy treat.
Sunflower Seeds: The Mood Booster
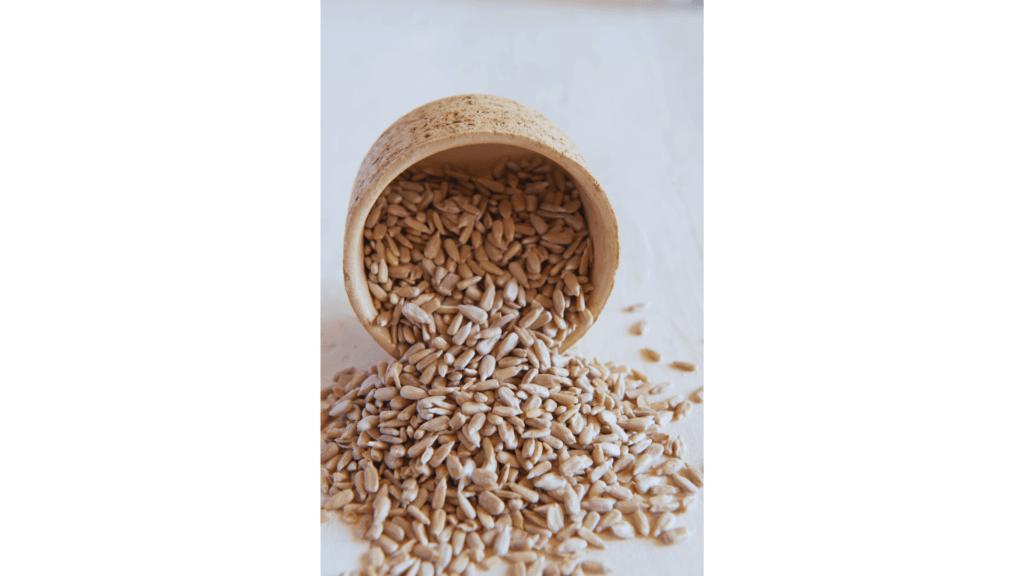

Sunflower seeds are rich in vitamin E, a powerful antioxidant that protects your skin and brain. They’re also high in selenium, which supports thyroid function and reduces oxidative stress.
Fun Fact: Sunflowers can grow up to 12 feet tall and were worshipped by the Aztecs as a symbol of the sun.
Pro Tip: Add sunflower seeds to your trail mix or sprinkle them on top of vegan yogurt.
Edamame: The Hormone Balancer
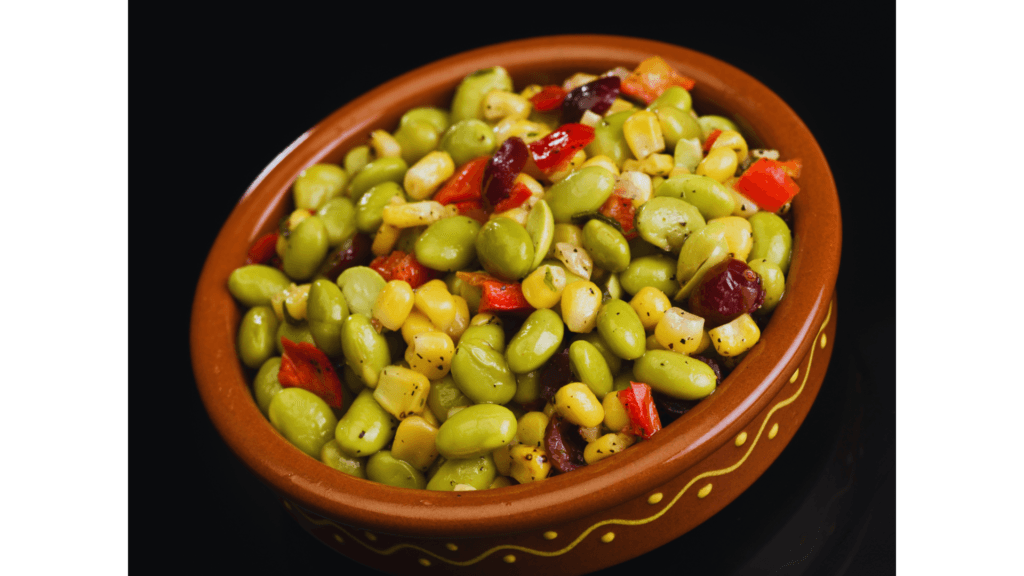

Edamame, or young soybeans, are rich in isoflavones, plant compounds that can help balance hormones and reduce the risk of certain cancers. They’re also a great source of protein and fiber.
Fun Fact: Edamame has been a staple in Japanese cuisine for over 2,000 years.
Pro Tip: Steam edamame and sprinkle with sea salt for a quick and satisfying snack
Black Beans: The Heart-Healthy Legume
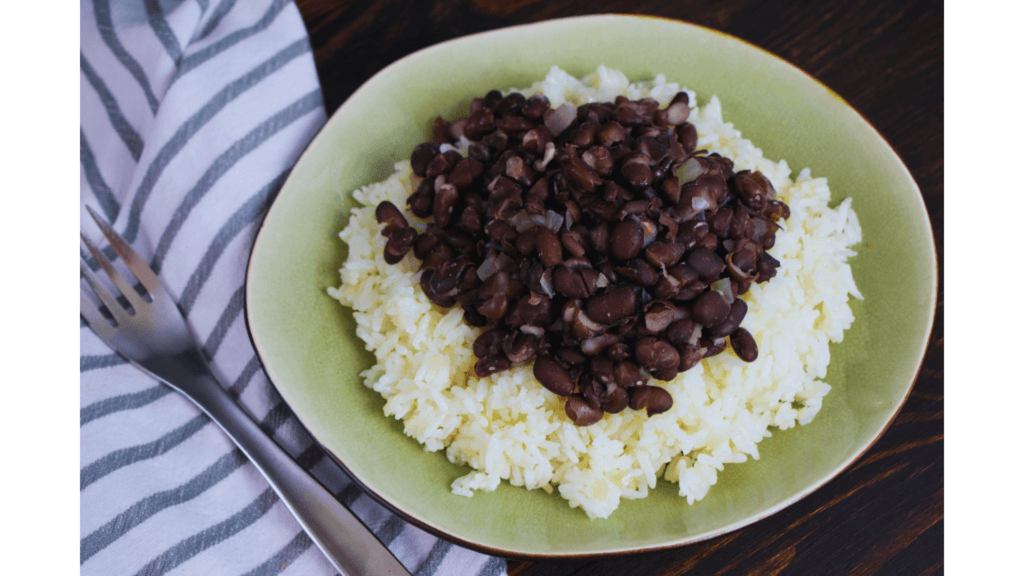

Black beans are high in anthocyanins, antioxidants that support heart health and reduce inflammation. They’re also a great source of fiber, which promotes healthy digestion.
Fun Fact: Black beans were a staple of the Aztec diet and were even used as a form of currency.
Pro Tip: Use black beans as a base for vegan burgers or add them to soups and stews.
Acai Berries: The Antioxidant Powerhouse
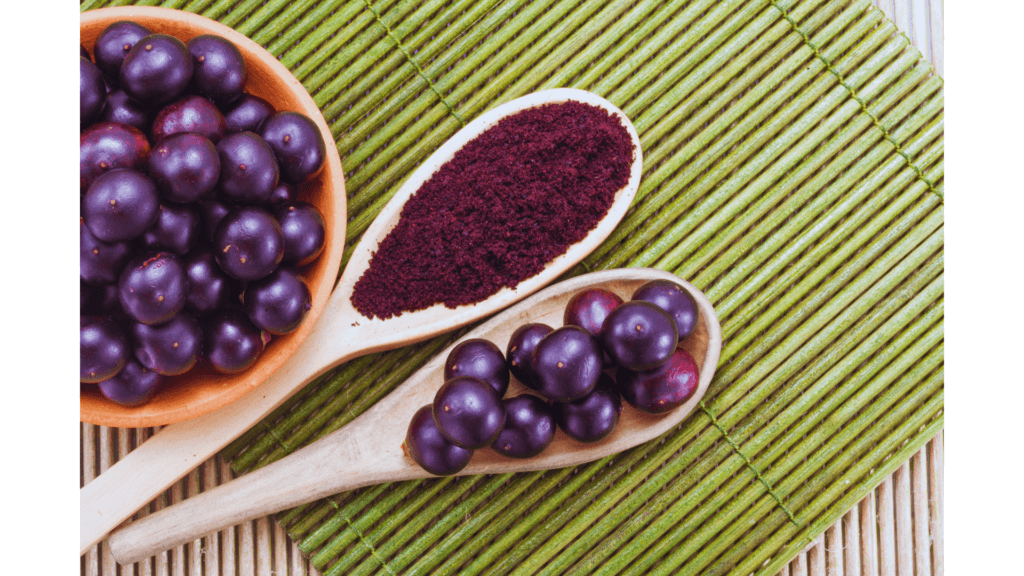

Acai berries are packed with polyphenols, antioxidants that fight inflammation and protect against chronic diseases. They’re also a great source of healthy fats and fiber.
Fun Fact: Acai berries grow on palm trees in the Amazon rainforest and have been a staple of indigenous diets for centuries.
Pro Tip: Blend acai berries into smoothie bowls and top with granola and fresh fruit.
Red Cabbage: The Immune Booster
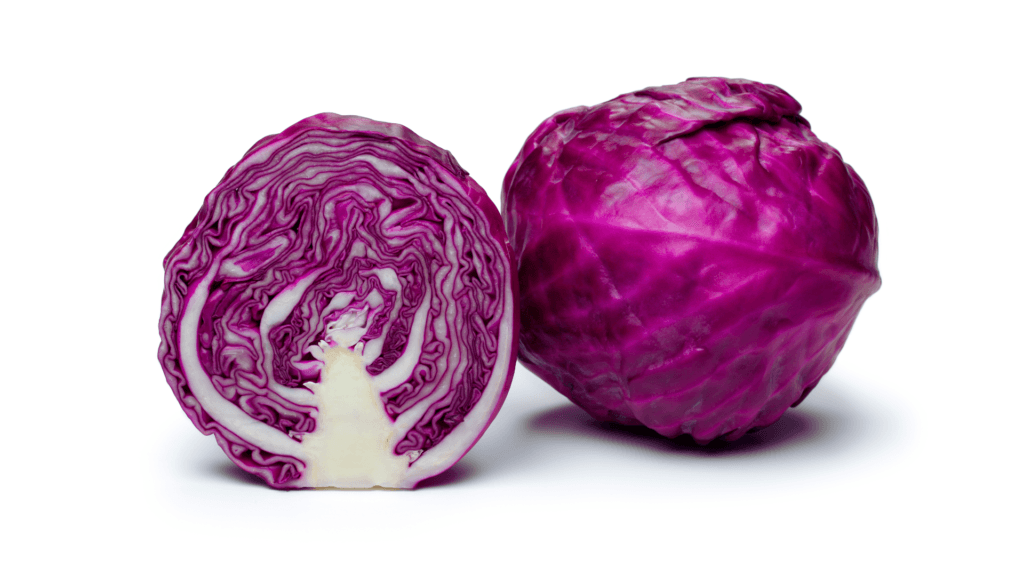

Red cabbage is rich in vitamin C and anthocyanins, which support immune function and reduce inflammation. It’s also a great source of fiber and vitamin K.
Fun Fact: Red cabbage can change color depending on the pH of the soil it’s grown in. Acidic soil turns it red, while alkaline soil turns it blue.
Pro Tip: Use red cabbage in slaws or ferment it to make sauerkraut
Goji Berries: The Longevity Fruit
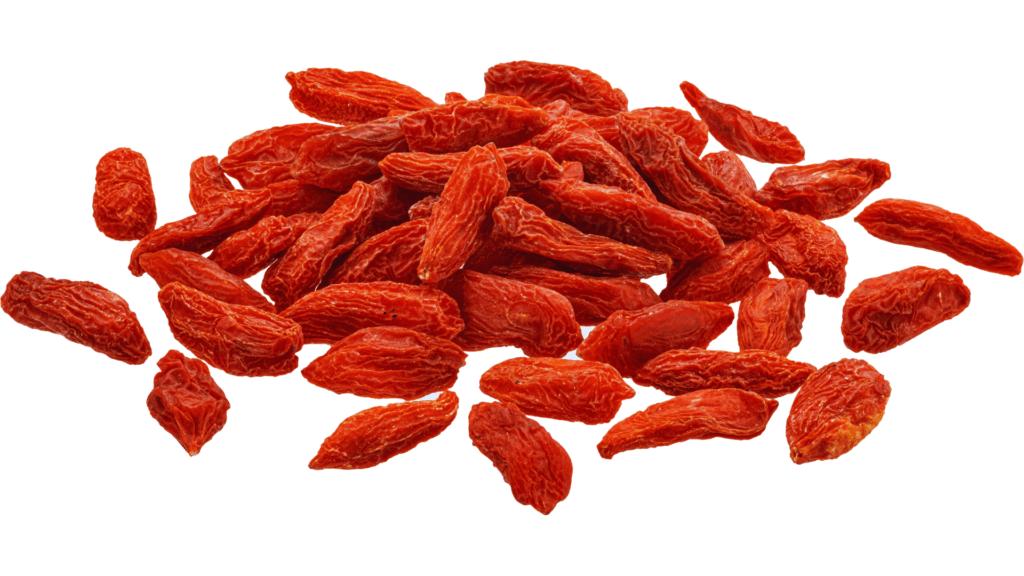

Goji berries are high in zeaxanthin, an antioxidant that supports eye health. They’re also rich in vitamin A and C, which boost immune function.
Fun Fact: Goji berries have been used in traditional Chinese medicine for over 2,000 years to promote longevity and vitality.
Pro Tip: Add goji berries to your trail mix or steep them in hot water for a nutrient-packed tea.
Seaweed: The Ocean’s Superfood
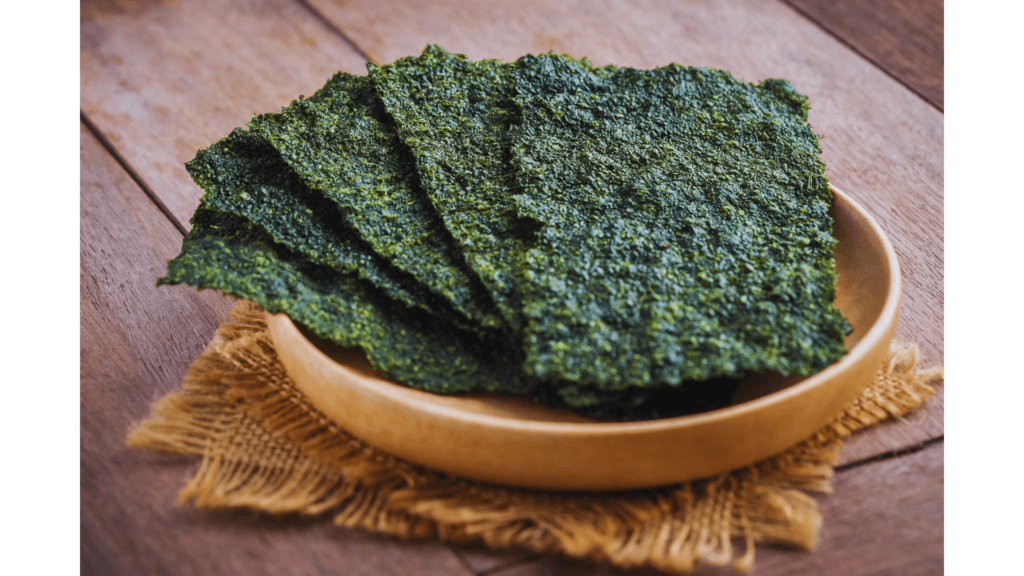

Seaweed is one of the few plant sources of iodine, a mineral essential for thyroid function. It’s also rich in calcium, iron, and antioxidants.
Fun Fact: Seaweed has been a staple in Asian diets for centuries and is even used in skincare products.
Pro Tip: Use nori sheets to make vegan sushi or add dried seaweed to soups and salads.
Peas: The Protein-Packed Legume
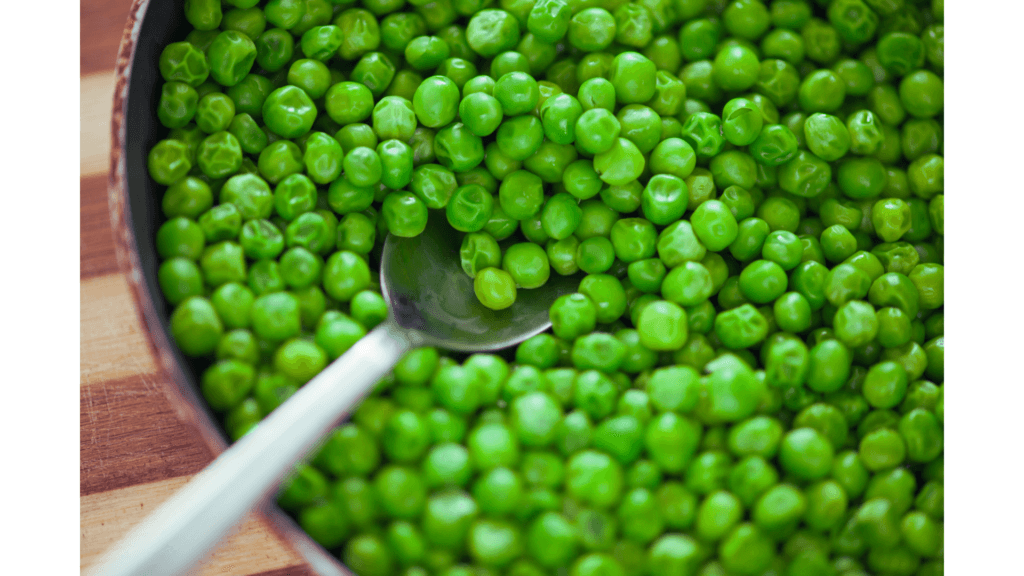

Peas are high in coumestrol, a compound that may reduce the risk of stomach cancer. They’re also a great source of protein and fiber.
Fun Fact: Peas were one of the first crops cultivated by humans, dating back over 10,000 years.
Pro Tip: Add peas to pasta dishes, risottos, or mashed potatoes for a nutrient boost.
Artichokes: The Digestive Aid

Artichokes are high in fiber and prebiotics, which support gut health. They’re also rich in antioxidants like quercetin.
Fun Fact: Artichokes were considered a delicacy in ancient Rome and were even used as an aphrodisiac.
Pro Tip: Steam artichokes and dip the leaves in a vegan aioli for a delicious appetizer.
Raspberries: The Anti-Inflammatory Berry

Raspberries are rich in ellagic acid, an antioxidant that has been shown to reduce inflammation and protect against cancer. They’re also a great source of fiber and vitamin C.
Fun Fact: Raspberries are part of the rose family, which explains their delicate aroma.
Pro Tip: Add raspberries to your morning smoothie or oatmeal for a sweet and tangy flavor.
Conclusion and Encouragement
Incorporating these 30 vegan superfoods into your diet isn’t just about eating healthy—it’s about thriving. Each of these foods brings something unique to the table, from boosting brainpower to protecting your heart. And the best part? They’re delicious and versatile, so you’ll never get bored.
Start small by adding one or two superfoods to your meals this week. Experiment with recipes, share your creations, and let us know how it goes in the comments below. Together, we can make vegan living not just sustainable but truly extraordinary.

