Why You Should Ditch Animal Protein: 14 Compelling Reasons for a Plant-Based Diet
As we navigate our dietary choices, it’s crucial to confront the unsettling truths about animal protein. While many people view meat and dairy as staples of a healthy diet, the reality is far more alarming. Here are compelling reasons to reconsider your consumption of animal protein, as they may pose serious health risks.

Understanding Animal Protein
Animal protein is a common source of nutrients in many diets, but it comes with a host of potential drawbacks. From increased disease risk to environmental concerns, there are several compelling reasons to reduce or eliminate animal protein consumption.
14 Reasons to Avoid Animal Protein
1. The IGF-1 Connection
One of the most troubling aspects of animal protein is its link to Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1). This hormone, which is naturally produced in our bodies, is crucial for growth and development. However, excessive levels, often spurred by a diet high in animal protein, have been associated with an increased risk of cancer. The more animal protein you consume, the higher your IGF-1 levels may rise, potentially putting you at greater risk for serious health issues.
2. The TMAO Threat
Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) is another alarming byproduct of consuming animal products. This compound is produced when gut bacteria metabolize certain nutrients found in red meat and fish. Elevated levels of TMAO have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular problems. The more animal protein you eat, the more TMAO your body may produce, raising serious concerns about your heart health.
3. Antioxidants: The Missing Link
While animal protein may provide certain nutrients, it lacks the antioxidants found in plant-based foods. Antioxidants are essential for combating oxidative stress and reducing inflammation in the body. A diet rich in animal products can lead to a deficiency in these vital compounds, leaving your body vulnerable to chronic diseases, including cancer and heart disease. The absence of antioxidants in a meat-heavy diet is a cause for alarm.
4. Heavy Metals in Fish
Fish is often touted as a healthy protein source, but it harbors hidden dangers. Many fish species are contaminated with heavy metals, such as mercury, which can accumulate in the body over time. Consuming these contaminated fish can lead to serious health problems, including neurological damage and developmental issues in children. The risks associated with heavy metals in fish should make anyone think twice before including it in their diet.
5. The Disturbing Truth About Dairy

Dairy consumption raises several health concerns that warrant attention. One significant issue is antibiotic resistance; many dairy cows are treated with antibiotics to prevent disease, which can lead to antibiotic residues in milk. This contributes to the growing problem of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, posing a risk to human health.
Additionally, the presence of somatic cells, often referred to as “cow pus,” is allowed in milk. These cells can indicate infection in cows, and while milk is pasteurized to kill harmful bacteria, the presence of these cells raises questions about the overall quality and safety of dairy products.
Moreover, many dairy products contain growth hormones, such as recombinant bovine somatotropin (rBST), which are used to increase milk production. These hormones may disrupt human hormonal balance and have been linked to various health issues, including increased cancer risk.
6. Kidney Damage from Hyperfiltration
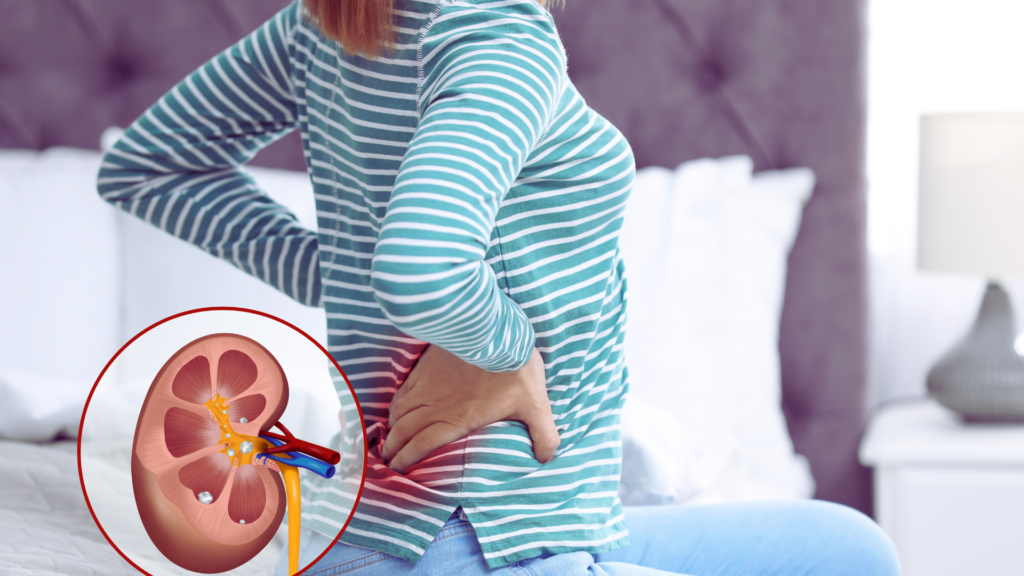
When you consume animal protein, your kidneys are forced into a state of hyperfiltration, dramatically increasing their workload. This can lead to kidney damage over time. Research shows that animal protein intake is associated with a decline in kidney function, while plant protein does not impose the same strain. This alarming difference highlights the potential for long-term kidney health issues linked to animal protein consumption.
7. Increased Risk of Heart Disease
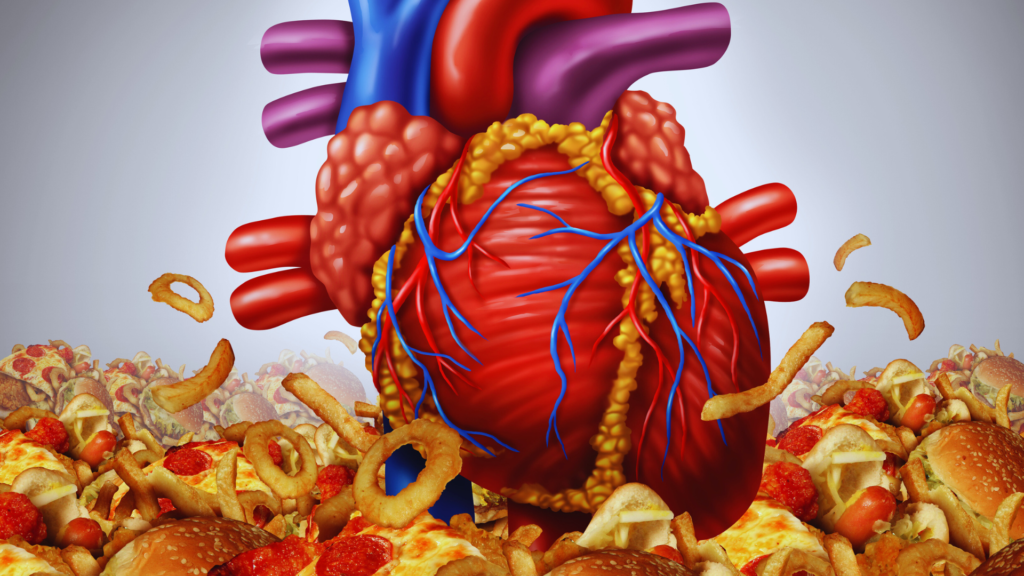
Diets high in animal protein are associated with an increased risk of heart disease. The saturated fats and cholesterol found in animal products can lead to arterial plaque buildup, raising blood pressure and increasing the likelihood of heart attacks and strokes. The evidence is clear: cutting back on animal protein could significantly improve cardiovascular health.
8. Antibiotic Resistance

The use of antibiotics in livestock is a significant public health concern. Consuming animal products can expose you to antibiotic-resistant bacteria, making infections harder to treat. This growing epidemic of antibiotic resistance is a direct consequence of our reliance on animal protein, putting your health at risk.
9. The Connection to Type 2 Diabetes

High animal protein intake has been linked to an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Studies show that those who consume large amounts of animal protein have a staggering 73 times higher risk of dying from diabetes compared to those who eat primarily plant-based diets. This shocking statistic should raise serious concerns about the impact of animal protein on metabolic health.
10. Chronic Inflammation
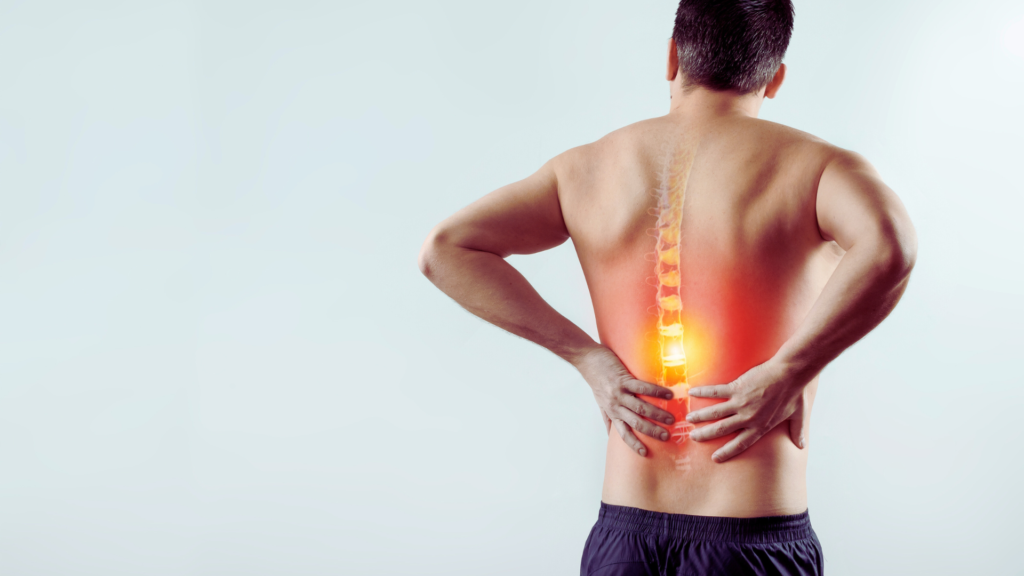
Animal protein can trigger inflammation in the body, which is a precursor to numerous chronic diseases. The inflammatory response caused by consuming meat can lead to conditions such as arthritis, heart disease, and even cancer. Reducing animal protein intake can help mitigate this inflammatory response and promote overall health.
11. The Dangers of Processed Meats

Processed meats, such as bacon and sausages, are classified as Group 1 carcinogens by the World Health Organization. This means there is sufficient evidence to suggest that consuming these products increases cancer risk. The alarming reality is that even small amounts of processed meats can have detrimental effects on your health.
12. The Impact on Bone Health
Contrary to popular belief, consuming animal protein may actually weaken bones. High protein diets can lead to increased calcium excretion through urine, potentially contributing to osteoporosis and fractures. A plant-based diet, rich in fruits and vegetables, can provide the necessary nutrients for stronger bones without the associated risks of animal protein.
13. Potential for environmental toxins

Animal foods can accumulate environmental toxins like PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls), dioxins and mercury that contaminate the environment. Plant foods have much lower levels of these toxins.
14. Elevated risk of dementia

A diet high in animal protein, especially meat, is associated with a greater risk of early death. Men eating more than 200g of meat per day had a 23% higher risk of death compared to those eating less than 100g.
Conclusion
There are numerous compelling reasons to ditch animal protein and embrace a plant-based diet. From improved health outcomes to environmental and ethical considerations, the benefits of reducing or eliminating animal protein are clear. If you’re ready to take the leap, start by gradually incorporating more plant-based foods into your diet and exploring the wide variety of delicious and nutritious options available. Your body, the planet, and the animals will thank you!

